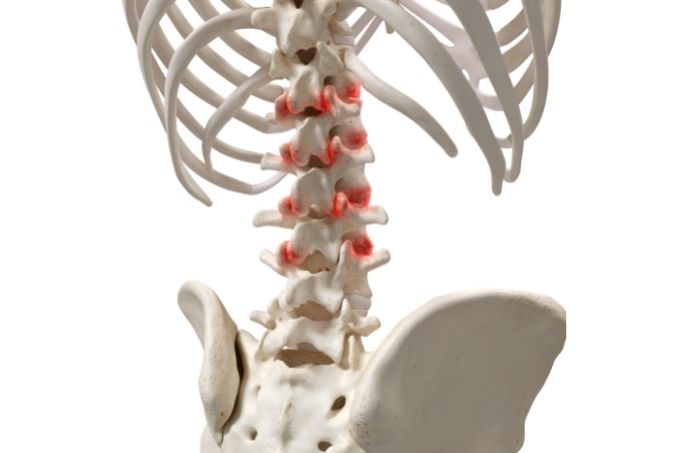
Think about all the things that your spine enables you to do; bend, turn, sit, stand upright, lean left and right, and so much more. All these activities are made possible, mainly by the facet joints situated in the spine. At times, as you do all these, you may have experienced pain. Did you know that this may be a likelihood of facet joint arthritis? Read on to find out more.
Other names: facet arthropathy, facet joint syndrome, Z joint arthritis, spinal osteoarthritis.
Spinal anatomy and arthritis
The spine is made up of bones referred to as vertebrae. The vertebrae are connected by joints known as the facet joints. The doctor can refer to these joints as facets, apophyseal or zygapophyseal joints. Like any other joints in the body, they function to offer healthy movement, flexibility, and stability for every motion segment. They work closely with the intervertebral discs, and therefore, the degeneration of one affects the other.
Facet joints have articular cartilage to offer them cushioning and prevent friction. If the cartilage that covers the facet joints wears down or thins out, spinal osteoarthritis occurs. This may result in osteophyte growth (bone spurs) and enlargement of these joints(hypertrophy). The condition occurs gradually over the years.
Types and causes
The cause is mainly dependent on what specific spinal point is affected.
Lumbar spinal osteoarthritis
It causes pain in the lower back and is the most common. The pain may be radiated or referred to the lower peripheries like the buttocks and thighs but not below the knee. Straightly standing up or even getting up from a seated position becomes difficult. Pain with an initiated motion is usually the most common symptom. The most prevalent risk factor or cause is a degenerative effect like aging but, trauma can also bring about the condition.
Cervical spinal osteoarthritis
The cervical spine is the top area of the spine. You will mostly feel pain in the neck and around the shoulder areas. The pain may restrict several ranges of motion, and particularly, head rotation becomes very difficult or almost impossible. You may also experience headaches. The most prevalent cause is trauma.
Thoracic spinal osteoarthritis
It causes pain within your mid-back. You may find that the ability to turn the entire body is restricted, especially when trying to turn right or left. It occurs mainly due to trauma. This type is the least common.
Risk factors
- Age– older people are at a greater risk.
- Trauma or an injury of the spinal zone’s facet joint(s).
- Wear and tear due to poor posture and activities such as heavy lifting.
- Bodyweight– Those with a BMI between 25-30 have a risk thrice higher, while those with a BMI of 30-35 are at risk five times greater.
- Sex- More women are prone to the condition, especially in the lumbar region of the spine.
- Degenerative disc disease.
- Heredity-A family history of disc degeneration and associated forms of arthritis.
Symptoms
- Pain in the affected spinal zone that worsens with leaning forward or bending. Pain from bending backward is more severe than when bending forward due to compression of the bones on the rear end.
- Tenderness in the soft tissue that surrounds the affected joint. The ligaments and muscles try to compensate for the pain, and as they “guard” (react to painful movements), they become more strained and tenser.
- Inflammation on the area around the affected facet joint due to friction.
- Back pain that becomes extreme with twisting or lifting.
- Stiffness on the affected spinal zone.
- Inability to move part of the neck, mid-back, or lower back.
Diagnosis
Pain is diagnosed chiefly using a historical evaluation and a physical exam. A physician can do an MRI, a CT scan, or an X-ray to provide spine imaging and reveal any consistent changes due to the condition. Where it is not clear whether the facet joint is causing pain, the facet joint will be injected with an anesthetic injection for a valuable diagnosis.
Treatment
Primarily, any form of treatment focuses on pain and stiffness relief and aids in allowing someone to stay active.
- Medication-The administration of over-the-counter drugs for pain relief. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs also downscale inflammation.
- Guided Physical Therapy to enable one to regain movement and strength of the spine using unique exercises.
- Spinal Anesthetic injections for relieving pain.
- Radiofrequency ablation– The use of radio-frequency waves to impair nerve function in the affected facet. Pain signals are not sent to the brain.
- Surgery- Spinal fusion, which fuses the affected spinal bones into one. Damaged facet joints are stopped from movement, and therefore, pain is alleviated.
Prevention
- Exercise regularly to keep the joints in motion through swimming, walking, or other low-impact activities.
- Keep a healthy body weight and eat healthily.
- Take proper precautions to avoid injury. Use protective gear for sports, lift things appropriately, and do not lift weighty objects.
- Always maintain the proper posture. Keep the back straight as you sit or stand.
- Use supplements such as calcium or Vitamin D to maintain healthy bones but always discuss them with your doctor before use.
Final Thoughts
With facet joint arthritis, somebody may feel acute or chronic pain in any region along the spine. With an accurate diagnosis you can, however, be sure about the point of your pain. There are several treatment and remedy options for pain management and also for motion restoration. Always seek the doctor’s help for more guidance about spinal pain.
Suggested articles:
– How To Prevent Arthritis In Hands – Symptoms and Prevention
– How To Prevent Arthritis In Knees – Info and Prevention
– Pisotriquetral Arthritis – Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
– Arthritis and Weather – How Does Weather Affect Arthritis?
– How To Prevent Arthritis – Arthritis Risk Factors and Its Prevention
– Rheumatoid Arthritis Nodules – Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Treatment)
– Hypertrophic Arthritis – Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
The Gout Eraser™: The all-natural guide for permanent gout removal
The Gout Eraser™ is a short, to the point guide on how to reverse gout symptoms without ever leaving your home. The guide goes into extensive detail on exactly what you need to do to safely, effectively and permanently get rid of gout, and you are GUARANTEED to see dramatic improvements in days if not hours.
To learn more about The Gout Eraser™ system, check out the following free video presentation: The Gout Eraser™