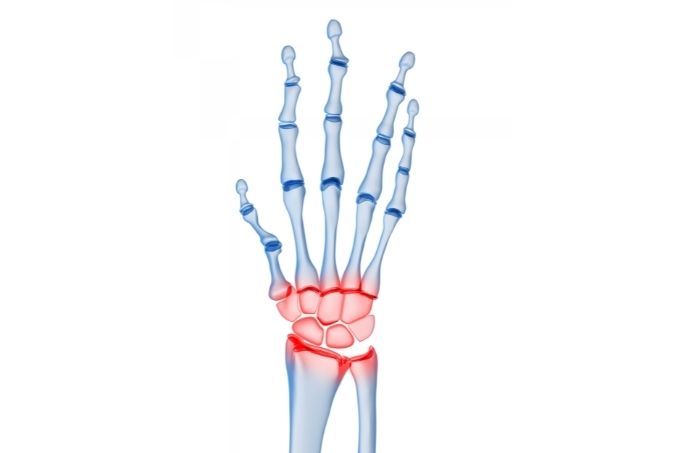
Arthritis is an inflammatory health condition that attacks bones by destroying the cartilage. This makes them to rub against each other to cause pain, particularly, within a joint. There is a wide variety of arthritic conditions, especially because, the condition may affect any joint of the body: large joints like the knee and small joints like the fingers.
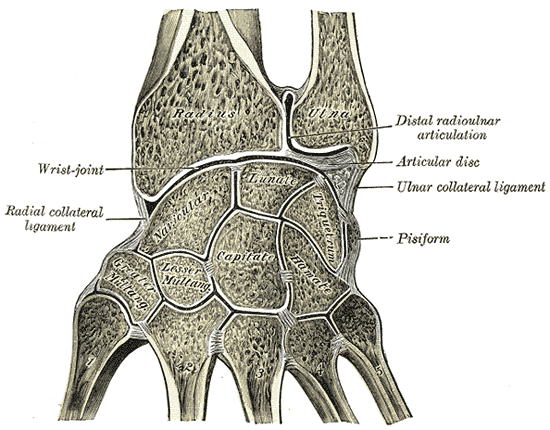
Pisotriquetral arthritis is arthritis of the pisotriquetral joint. At times, this condition can be referred to as osteoarthritis of the pisotriquetral joint. This is the small joint on the ulnar side of the wrist. With this condition, you experience pain over your wrist (pisiform). The pisiform bone is a small and pea-shaped sesamoid bone that is part of the eight carpal or wrist bones. It is situated where the ulna (a forearm bone) connects with the wrist (the side of the little finger).
The pisiform achieves stability from tendon and ligament attachments. The pisotriquetal joint attains mobility through the use of a strong but, loose capsule. If the wrist has denudation of the bone, the pain is very severe. This is because the cartilage has no nerve supply.
Causes
- Trauma- Where the pisotriquetral joint suffers acute or chronic trauma.
- Tendinitis from flexor carpi ulnaris insertion.
- Age. The condition is also degenerative and therefore, it can be prevalent among the older population. Old age may damage the articular cartilage.
- Bone fractures.
Symptoms
- Pain over the pisiform that can worsen with grinding of the joint and pressure.
- Irritation when you perform tasks that involve the wrist.
- Tenderness or swelling over the pisiform.
- Some ulnar nerve symptoms can be experienced, such as weakness, tingling, and numbness within the little finger. You may also experience these symptoms along the outside of your ring finger.
- A limited range of motion for the joint.
Suggested article: What Does Arthritis Feel Like?
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is mainly based on a clinical examination. Radiographs may be used to reveal its evidence but, they are not sufficient. They can also be misinterpreted; hence, other diagnostic tools are involved. MRI can be used to reveal any degeneration of the wrist tendon and sometimes, the inflammation. CT scans and Microscopy assessment can also be done to show the degree of effect.
Treatment and Management
There are several treatment options for the condition that include conservative measures.
Medication– Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be administered for treatment. Pain relievers such as acetaminophen are recommended for limited use or as needed. Corticosteroids can also be used to reduce inflammation.
Steroid Injections– The pisotriquetral joint can be injected with steroid injections for pain relief. Steroids are used when medication does not control inflammation. They can weaken ligaments and joints and therefore, they are repeated minimally.
Physical Therapy and Exercising– Exercises promote strength and allow the joint to stretch. This improves function and reduces the symptoms. Treatment requires an understanding and knowledge of the pisiform, triquetrum, and other wrist surrounding structures. Therefore, where physical therapy is used for treatment, the therapist must be aware of how all these functions.
This will prevent further escalation of the condition.
Splints and braces– Protective splints and braces are used to support the affected joint, offer stability, reduce strain and deformity, and to promote proper joint alignment. These must be discussed with a hand or occupational therapist. Wearing them for too long can weaken the muscles.
Rest– Regular rest can relieve pain and lessen inflammation.
Heat and cold therapy– Cold packs reduce pain and swelling, while heat will reduce stiffness. Alternate them and do not apply for longer than 20 minutes each time. Use a towel to create a barrier. Do not apply directly.
Surgery– Surgery is conducted where the other conservative treatments are unsuccessful or, where initial nonoperative treatments fail. This involves excision of the pisiform bone (pisiformectomy) for complete pain relief. Surgery can however bring about other functional limitations.
Final Thoughts
It is fairly common to feel pain within the ulnar side of the wrist and it may result from a wide variety of issues. It can also be a sign of pisotriquetral arthritis. Since you may be uncertain about what is causing you pain, it is necessary to get a diagnostic investigation. This will allow you to commence on accurate treatment options and a management plan.
Suggested articles:
– Facet Joint Arthritis (Spinal Osteoarthritis) – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
– How To Prevent Arthritis In Hands – Symptoms and Prevention
– Arthritis and Weather – How Does Weather Affect Arthritis?
– Arthritis Vs Arthralgia – Everything You Need to Know
– Postpartum Arthritis – Arthritis After Pregnancy
– How To Prevent Arthritis – Arthritis Risk Factors and Its Prevention
– Rheumatoid Arthritis Nodules – Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Treatment
The Gout Eraser™: The all-natural guide for permanent gout removal
The Gout Eraser™ is a short, to the point guide on how to reverse gout symptoms without ever leaving your home. The guide goes into extensive detail on exactly what you need to do to safely, effectively and permanently get rid of gout, and you are GUARANTEED to see dramatic improvements in days if not hours.
To learn more about The Gout Eraser™ system, check out the following free video presentation: The Gout Eraser™