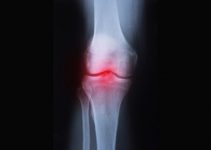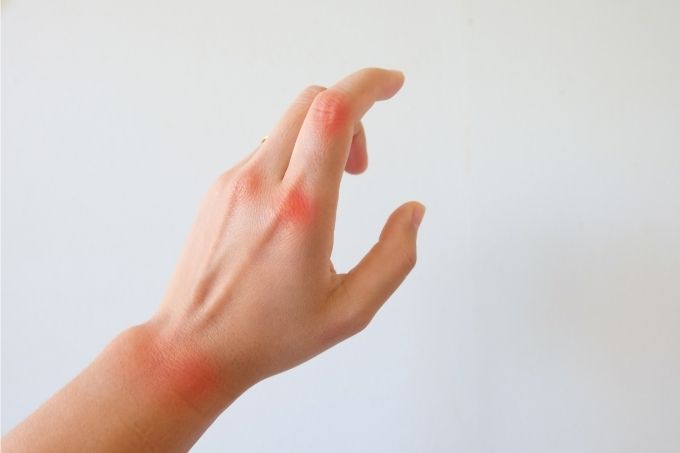
Arthritis is a term used to refer to any condition or disease that involves pain and/or stiffness of the musculoskeletal system. It is a combination of many diseases. Hypertrophic arthritis is a very common disorder of the joints and is a degenerative joint disease. It is a variant of osteoarthritis and is mostly characterized by the formation of periarticular osteophyte. Its occurrence increases with age.
Occurence
Anyone above 20 or 30 years may experience degenerative changes within the cartilages of the joints that bear weight. With osteoarthritis, the articular cartilage is eroded to turn soft, thinned, or frayed. The progressive degradation of the cartilage results in the loss of joint movability, function and chronic pain is experienced.
Cartilage refers to the firm and rubbery tissue which works to cushion joint bones. It allows for bones to move smoothly over each other. If it breaks and eventually wears off, the bones rub, and this brings about swelling and stiffness. If the condition worsens, extra bone or bone spurs may be created around the affected joint. The muscles and ligaments that exist around that particular joint may turn stiffer and weaker. Before 55, the condition equally occurs in men and women but, after 55, it is more prevalent in women.
Hypertrophic Arthritis is very common, particularly because the risk increases with age. However, the symptoms can be managed with the practices and treatments.
Causes
Medical conditions– This form of arthritis can be brought about by; some bleeding disorders that may lead to joint bleeding, for example, hemophilia, any disorder that can possibly block the blood supply to a joint or bring about a bone death like avascular arthritis, and some forms of arthritis-like pseudogout, chronic gout, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Genetics– It tends to run in families.
Joint injuries and trauma may bring about osteoarthritis in later life, joint cartilage and ligaments included.
Obesity and being overweight– These result in an increased risk in the joints of the hip, knee, ankle, and foot. More weight leads to more wear and tear.
Certain jobs– Jobs that entail a lot of kneeling, squatting, lifting, and walking.
Sports – Sports that may directly impact a joint like football, and those that entail twisting like soccer and basketball.
Symptoms
- Intense pain worsens with exercise, joint pressure, and usage of the affected joint.
- Less movement.
- Swelling of the joint.
- The development of venous stasis and blood clots.
- Where symptoms are observed in the hip, the hip muscles’ function is impaired.
Suggested article: What Does Arthritis Feel Like?
Exams, Tests, and Treatment
A health care provider will usually diagnose the condition by conducting an examination that may confirm the symptoms of arthritis. Blood tests do not fully help during diagnosis.
Cure is not available, but the symptoms are controllable. Treatments will usually be used to turn the symptoms mild to not lead to further complications. You may prevent and treat the symptoms through;
Medication– Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or the administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Lifestyle adjustments– Remaining active and exercising, healthy eating, getting enough rest, focusing on losing weight if you are overweight, and preventing the joints from injury.
Suggested article: Top 12 Foods to Avoid with Arthritis – The ULTIMATE List
Physical therapy to improve muscle strength and increase motion within the stiff joints.
Massage therapy for pain relief. Always involve a licensed professional who can work on sensitive joints.
Using splints and braces to offer support to weakened joints, as recommended by your doctor or therapist. This is because some may limit joint movement and others may shift the joint pressure.
Acupuncture to relieve pain on particular points of an affected joint.
Surgery for replacement or repair of damaged joint(s).
Suggested article:
– How To Prevent Arthritis In Hands – Symptoms and Prevention
– Rheumatoid Arthritis Nodules – Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Treatment
– Postpartum Arthritis – Arthritis After Pregnancy
– How To Prevent Arthritis – Arthritis Risk Factors and Its Prevention
– Soap In Bed For Arthritis – How Does Soap Work For Arthritis?
– Facet Joint Arthritis (Spinal Osteoarthritis) – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
– Arthritis and Weather – How Does Weather Affect Arthritis?
The Gout Eraser™: The all-natural guide for permanent gout removal
The Gout Eraser™ is a short, to the point guide on how to reverse gout symptoms without ever leaving your home. The guide goes into extensive detail on exactly what you need to do to safely, effectively and permanently get rid of gout, and you are GUARANTEED to see dramatic improvements in days if not hours.
To learn more about The Gout Eraser™ system, check out the following free video presentation: The Gout Eraser™